What is an address verification service?
An address verification service (AVS) is an automated system used in online transactions to verify a customer’s billing address. It compares the address provided during checkout with the address on file at the card-issuing bank, helping merchants detect and prevent potential credit card fraud.
How do address verification services work?
Address Verification Services protect merchants, issuers, and card holders against credit card fraud and the accompanying fraud related chargebacks. Card issuers check certain criteria before authorizing a transaction. These include whether the account has an adequate balance for the payment, whether the card is valid, and if the CVV code and address provided match those on file. AVS refers to the address verification part of this procedure.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how AVS works:
1.Customer input: During an online transaction, the customer enters their billing address along with their credit card information.
2.Data transmission: The merchant’s payment gateway sends this address information, along with the transaction details, to the card-issuing bank.
3.Address comparison: The bank’s AVS compares the numeric portions of the street address and the ZIP code provided by the customer against the information they have on file.
4.Response generation: Based on this comparison, the AVS generates a single letter response code.
5.Code interpretation: The merchant receives this code, which indicates the level of match between the provided address and the one on file.
6.Decision making: The merchant can then use this information to decide whether to proceed with, flag, or decline the transaction.
AVS codes typically indicate whether there’s a full match, partial match, or no match for the address and ZIP code. For example, a code might show that the ZIP code matches but the street address doesn’t. If a match is only partial, further verification may be required to authenticate the transaction. Usually, AVS is employed as part of a multilayered fraud prevention system, which might also include CVV validation codes, IP address verification, biometric analysis, and device authentication.
What is their role in protecting merchants?
Address Verification Services play a crucial role in protecting merchants and cardholders from fraudulent transactions – and they are becoming more important year on year. Recent research shows that payment fraud attempts rose by 71% in 2023, with 36% of companies reporting fraud-related financial losses in excess of $1m. AVS protects against the rising cost of fraud for merchants by fulfilling the following roles:
1.Fraud prevention: By verifying the billing address, AVS helps identify potential cases of credit card fraud where the perpetrator doesn’t have access to the cardholder’s correct address.
2.Risk assessment: AVS provides an additional data point for merchants to assess the risk of a transaction. A mismatch doesn’t necessarily indicate fraud, but it can prompt the merchant to conduct further verification.
3.Chargeback reduction: By helping to prevent fraudulent transactions, AVS can significantly reduce the number of chargebacks a merchant faces, protecting their revenue and reputation.
4.Customer trust: Implementing AVS demonstrates to customers that the merchant takes security seriously, potentially increasing customer confidence and loyalty.
Liability shift: In some cases, using AVS can shift liability for fraudulent transactions from the merchant to the card issuer, providing an additional layer of protection.
Should your business enable AVS?
AVS is not mandatory for merchants, but it is highly recommended. These systems add an extra layer of security to your transaction process, making it more difficult for fraudsters to use stolen credit card information. This enhanced fraud prevention capability can significantly reduce your exposure to chargebacks by catching potentially fraudulent transactions before they’re processed. AVS is also typically offered for free by acquirers and issuers.
How can you set up AVS for your business?
Setting up AVS for your business is typically a straightforward process:
1.Contact your payment processor or gateway provider: Most major payment processors and gateways offer AVS as part of their services.
2.Enable AVS in your payment settings: This usually involves toggling a setting in your payment gateway’s dashboard or admin panel.
3.Integrate AVS into your checkout process: Ensure your checkout form collects the necessary address information from customers.
4.Set up AVS response handling: Decide how your system will handle different AVS response codes (e.g., which codes will result in transaction approval, flagging, or decline).
Monitor and adjust: Regularly review your AVS performance and adjust your settings as needed to balance fraud prevention with customer experience.
Problems with AVS: Fraudulent verification and friendly fraud
While AVS is a powerful tool, it’s not without its limitations. AVS can sometimes generate false declines or partial declines, requiring the merchant to use further validation methods. This can lead to lost sales and reputational damage if not handled quickly. Addresses, CVV and IP, can also become compromised through data breaches and poor handling, limiting the effectiveness of these verification methods.
While AVS and other fraud prevention tools are crucial first lines of defense, they can’t prevent fraud or chargebacks from occurring. In cases of ‘friendly fraud’, card holders provide correct addresses and CVVs, but knowingly or unknowingly dispute legitimate transactions. Friendly fraud is a growing problem for businesses, with research showing a 19% increase in 2023, and 55% of disputes departments reporting that friendly fraud is ‘extremely challenging.
Friendly fraud is usually handled through chargeback procedures, where the merchant provides evidence to the issuer to prove the legitimacy of the transaction. However, this process is often time and labor-intensive, and can result in losses of up to 25% of annual income if several chargebacks are lost. Card schemes may also issue fines and penalties if merchants accrue high rates of chargebacks.
Justt offers protection where other defenses fail
While AVS and other verification methods offer little protection against friendly fraud, modern chargeback solutions mitigate much of the inherent risk by significantly reducing rates of lost chargebacks. Justt offers a fully automated and affordable solution that handles chargebacks using AI-powered technology, reducing the time and resources your team needs to spend on dispute resolution, and recovering large amounts of revenue through chargebacks won.
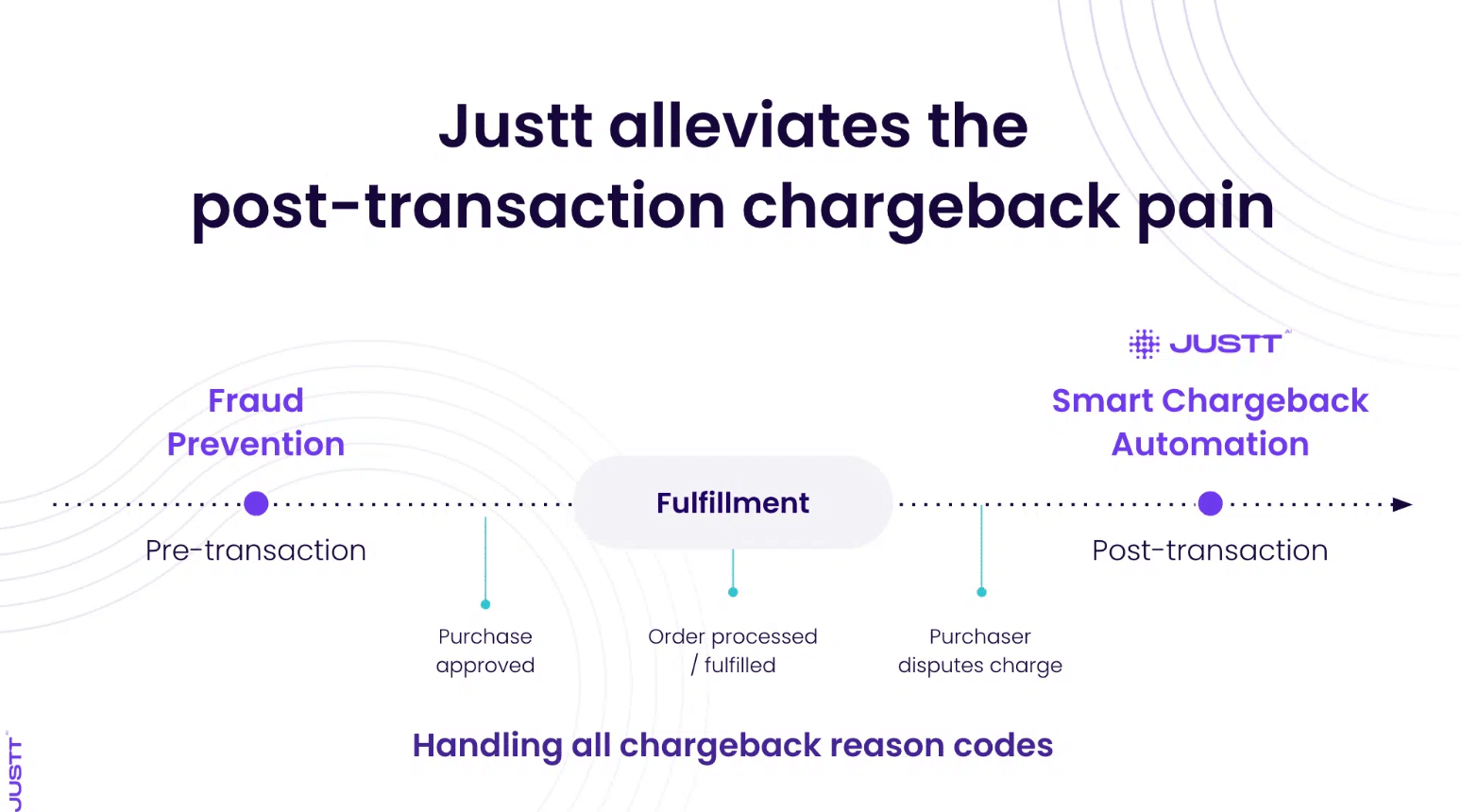
Justt’s machine learning pulls data from acquirers, merchants, and third party sources to create dynamic arguments in support of your chargeback claims. These arguments are tailored to the dispute type and individual quirks of the issuer who will decide the case – increasing win rates significantly. The system learns from each case, continuously improving its performance and adapting to new fraud patterns and chargeback reasons. Additionally, Justt’s analytics provide valuable insights into your chargeback patterns, helping you refine your fraud prevention strategies, including your use of AVS.
By combining robust front-end fraud prevention measures like AVS with Justt’s chargeback management solution, merchants can create a comprehensive defense against true and friendly fraud. This multi-layered approach ensures maximum protection for revenue and reputation, while near-total automation in each instance means that your business remains free to tackle more strategic concerns.