What is a Card Issuer?
A card issuer, also known as an issuing bank, is a financial institution that provides credit or debit cards to consumers and businesses. Examples of card issuers include banks like JPMorgan Chase, Bank of America, and Citibank, as well as credit unions and prepaid card providers. These institutions are responsible for approving credit card applications, setting credit limits, and maintaining cardholder accounts. They also handle billing, collect payments from cardholders, and bear the financial risk if a cardholder defaults on their payments.
What merchants need to know about card issuers
- Card issuers are the primary parties responsible for authorizing transactions. When a customer makes a purchase, the issuer decides whether to approve or decline the transaction based on factors like available credit, account status, and potential fraud indicators.
- In the event of a chargeback, the card issuer is the first point of contact for the cardholder. The issuer makes an initial decision to pursue the chargeback based on evidence provided by the card holder, after which the payment amount is debited from the merchant and returned to the card holder. The issuer is also responsible for examining the evidence merchants may provide to dispute the chargeback.
- Different card issuers may have varying policies regarding chargebacks, fraud prevention, and dispute resolution. Understanding these differences can help merchants better manage their payment processes and customer interactions.
- Card issuers often offer rewards programs, cashback, or other incentives to cardholders, which can influence consumer spending behavior and payment preferences.
- Some card issuers specialize in specific market segments (e.g., high-net-worth individuals, students, small businesses). Analyzing which card issuers your customers make payments with can provide valuable first-party data, allowing merchants to better understand the demographics and spending patterns of their cardholders.
What role do card issuers play in the financial ecosystem?
Card issuers assume financial responsibility for all transactions made on card holders’ accounts, and interact with several other institutions during each card transaction. When a cardholder makes a purchase, the transaction details flow from the merchant through their acquiring bank to the card scheme (e.g. Visa, Mastercard). The card scheme then routes the authorization request to the card issuer. The issuer verifies the account status, checks available funds, and conducts fraud checks before approving or declining the transaction.
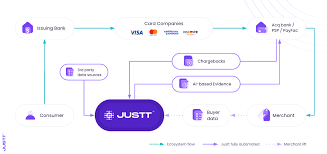
This response travels back through the same chain to complete the sale. Later, during settlement, the card issuer transfers funds to the acquiring bank via the card scheme, which then deposits the money into the merchant’s account. Other roles performed by card issuers include:
1.Credit extension: They evaluate creditworthiness and extend lines of credit to consumers and businesses.
2.Fraud prevention: They employ sophisticated fraud detection systems to protect both cardholders and merchants from unauthorized transactions.
3.Consumer financial services: Many card issuers offer additional financial products and services, such as savings accounts, loans, and investment options.
4.Data analytics: Card issuers collect and analyze transaction data, providing valuable insights into consumer spending patterns and economic trends.
5.Regulatory compliance: They ensure adherence to various financial regulations, including anti-money laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements.
6.Dispute resolution: Card issuers manage the chargeback process, mediating disputes between cardholders and merchants.
Card issuers vs. card schemes vs. PSPs
Card issuers are distinct from – but often confused with – card schemes (such as Visa and Mastercard). Both institution types work in partnership to offer branded payment cards typically bearing each logo. While the issuer extends credit to the cardholder and manages the account, the card scheme provides and regulates the payment infrastructure and processes card payments. It should be noted that, while relatively uncommon, some companies, like American Express and Discover, act as both card issuers and card schemes.
Payment service providers (PSPs) also work closely with – but are distinct from – card issuers and card schemes. Like issuers and schemes, they act as intermediaries between the card holder and merchant. PSPs provide software and hardware that allows merchants to take payment from card holders, offering services such as payment gateways, payment processing, merchant accounts, and fraud prevention and reporting.
Card Issuers (e.g., JPMorgan Chase, Citibank)
- Provide cards directly to consumers
- Manage cardholder accounts and credit lines
- Handle billing and payment collection
- Bear the financial risk of cardholder defaults
- Offer customer service to cardholders
Card Schemes (e.g., Visa, Mastercard):
- Operate the payment networks that process transactions
- Set interchange fees and network rules
- Provide the technology infrastructure for payment processing
- Establish security standards for the payment ecosystem
Payment Service Providers (PayPal, Square, Shopify)
- Provide a unified platform to accept various payment methods.
- Connect merchants to card networks and financial institutions for payment processing.
- Handle transaction authorization, settlement, and reconciliation on behalf of merchants.
- Implement fraud detection and security features to protect transactions.
- Offer reporting tools and analytics to help merchants manage their payment processes and understand transaction data.
How do different card issuers impact chargebacks?
While chargebacks can prove devastating to merchants, costing up to 25% of net income, the chargeback dispute process can also be very costly and time-intensive. This is in part due to the complexities of consolidating and providing evidence to card issuers. Each issuer operates in different ways, with particular biases, time constraints, and evidence preferences. The template formats of most chargeback dispute solutions totally fail to account for these vital distinctions, leading to high rates of lost cases.
How does Justt work with card issuers?
Justt’s dynamic chargeback representments deliver maximal win rates. This is because evidence is tailored to the nuances of the particular card issuer, reason code, card scheme and more. Detailed knowledge of how each card issuer operates is combined with AI learning that discerns which kinds of arguments are most successful with each issuer, and optimizes evidence accordingly. Justt’s automated system instantly draws data from acquiring banks, the merchant, and third party sources – presented as the optimal evidence to win the dispute.
No business can afford to take risks with chargebacks. Nor is it feasible for merchants to learn the intricacies of how every issuer responds to chargebacks – especially not when Justt can do it automatically, hyper-effectively, and at a fraction of the cost.
Speak with us today to start securing your hard-earned revenue.